HTML DOM
Every webpage can be considered an object, and it exists inside a browser window. We can access the webpage using the web browser, which needed to be connected to the internet. The DOM is an acronym for the Document object model. A Document object denotes the HTML document that is displayed in that window. The document object model is made up of several properties that refer to other objects, allowing you to modify the document’s content.
The process by which the content of the document is accessed is called the Document Object Model, or DOM. The objects are organized in a hierarchy. The hierarchical structure is used to organize objects in a web document.
- Window – It is the first in the hierarchy. It is the utmost element of the object hierarchy.
- Document – When an HTML document loads into a window that it becomes a window object. The document includes the contents of the page.
- Elements – These denote the content on the webpage. For example – Title, text box, etc.
- Nodes – These are often elements, but they also are attributes, comments, text, and other DOM types.
Finding DOM Elements
A document can contain many attributes, and sometimes we need to search for particular attributes. The dart:html library provides the querySelector function to search elements in the DOM.
Element querySelector(String selector); The querySelector() function returns the first element that matches the specified group of the selector.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<meta http-equiv = "X-UA-Compatible" content = "IE = edge">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device-width, initial-scale = 1.0">
<meta name = "scaffolded-by" content = "https://github.com/google/stagehand">
<title>DemoWebApp</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "styles.css">
<script defer src = "main.dart" type = "application/dart"></script>
<script defer src = "packages/browser/dart.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
<div id = "output"></div>
</h1>
</body>
</html> Main.dart
import 'dart:html';
void main() {
querySelector('#output').text = 'Your Dart web dom app is running!!!.';
} Event Handling
The dart:html library provides the onClick event for DOM Elements. The syntax shows how an element could handle a stream of click events.
querySelector('#Id').onClick.listen(eventHanlderFunction); The querySelector() function returns the element from the given DOM and onClick.listen() will take an eventHandler method which will be invoked when a click event is raised.
Let’s now take an example to understand the concept of Event Handling in Dart.
TestEvent.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<meta http-equiv = "X-UA-Compatible" content = "IE = edge">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device-width, initial-scale = 1.0">
<meta name = "scaffolded-by" content ="https://github.com/google/stagehand">
<title>DemoWebApp</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "styles.css">
<script defer src = "TestEvent.dart" type="application/dart"></script>
<script defer src = "packages/browser/dart.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "output"></div>
<h1>
<div>
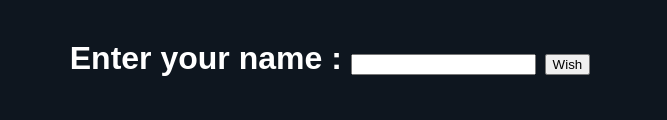
Enter your name : <input type = "text" id = "txtName">
<input type = "button" id = "btnWish" value="Wish">
</div>
</h1>
<h2 id = "display"></h2>
</body>TestEvent.dart
import 'dart:html';
void main() {
querySelector('#btnWish')?.onClick.listen(wishHandler);
}
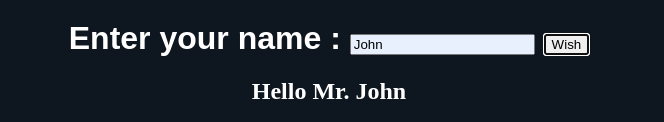
void wishHandler(MouseEvent event) {
String name = (querySelector('#txtName') as InputElement).value.toString();
querySelector('#display')?.text = 'Hello Mr. ' + name;
}
Output: